Product Summary
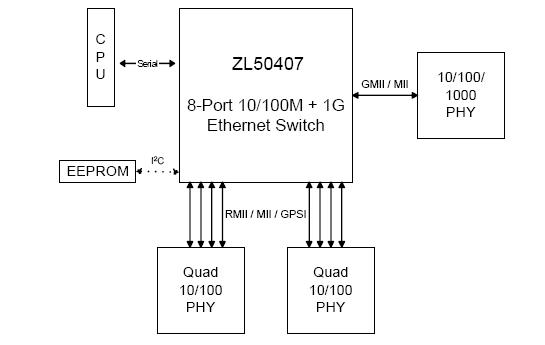
The ZL50407GD is a low density, low cost, high performance, non-blocking Ethernet switch chip. A single chip provides 8 ports at 10/100 Mbps, 1 uplink port at 10/100/1000 Mbps, and a CPU interface for lightly managed and unmanaged switch applications. The chip supports up to 4 K MAC addresses and port-based Virtual LANs (VLANs). The ZL50407GD provides the ability to monitor a link, detect a simple link failure, and provide notification of the failure to the CPU. The CPU can then failover that link to an alternate link. The ZL50407GD supports 8 groups of port trunking/load sharing. Each group can contain up to 8 ports. Port trunking/load sharing can be used to group ports between interlinked switches to increase the effective network bandwidth.
Parametrics
ZL50407GD absolute maximum ratings: (1)Storage Temperature: -65℃ to +150℃; (2)Operating Temperature: -40℃ to +85℃; (3)Maximum Junction Temperature: +125℃; (4)Supply Voltage VCC with Respect to VSS: +2.95V to +3.65V; (5) Supply Voltage VDD with Respect to VSS: +1.60V to +2.00V; (6) Voltage on 5 V Tolerant Input Pins: -0.5V to (VCC + 2.5V); (7) Voltage on Other Pins: -0.5V to (VDD + 0.3 V).
Features
ZL50407GD features: (1)Integrated Single-Chip 10/100/1000 Ethernet Switch; (2)Eight 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiating Fast Ethernet (FE) ports with RMII, MII, GPSI, Reverse MII & Reverse GPSI interface options; (3)One 10/100/1000 Mbps auto-negotiating port with GMII & MII interface options, that can be used as a WAN uplink or as a 9th port; (4)Operates stand-alone or can be cascaded with a second ZL50407 to reach 16 ports; (5)Embedded 2 Mbits (256 KBytes) internal memory; (6)supports up to 4 K byte frames; (7)L2 switching; (8)MAC address self learning, up to 4 K MAC addresses using internal table; (9)Supports the following spanning standards: IEEE 802.1D spanning tree, IEEE 802.1w rapid spanning tree; (10)Supports Ethernet multicasting and broadcasting and flooding control; (11)VLAN Support; (12)Supports port-based VLAN; (13)CPU access supports the following interface options: Serial interface in lightly managed mode, or in unmanaged mode with optional I2C EEPROM interface; (14)Failover Features; (15)Rapid link failure detection using hardware-generated heartbeat packets; (16)link failover in less than 50 ms; (17)Rate Control (both ingress and egress); (18)Bandwidth rationing, Bandwidth on demand, SLA (Service Level Agreement); (19)Smooth out traffic to uplink port; (20)Ingress Rate Control: Back pressure, Flow Control, WRED (Weighted Random Early Discard), Egress Rate Control, Down to 16 kbps Rate Control granularity; (21)Per queue traffic shaper on uplink port; (22)Packet Filtering and Port Security; (23)Static address filtering for source and/or destination MAC; (24)Static MAC address not subject to aging; (25)Secure mode freezes MAC address learning (each port may independently use this mode); (26)Supports port authentication (IEEE 802.1x); (27)QoS Support; (28)Supports IEEE 802.1p/Q Quality of Service with 2 transmission priority queues (4 for uplink port), with strict priority and/or WFQ service disciplines; (29)Provides 2 levels of dropping precedence with WRED mechanism; (30)User controls the WRED thresholds.; (31)Buffer management: per class and per port buffer reservations; (32)Port-based priority: VLAN priority in a tagged frame can be overwritten by the priority of Port VLAN ID; (33)Supports per-system option to enable flow control for best effort frames even on QoS enabled ports; (34)Classification based on:; (35)Port based priority; (36)VLAN Priority field in VLAN tagged frame; (37)DS/TOS field in IP packet; (38)UDP/TCP logical ports: 8 hard-wired and 8 programmable ports, including one programmable range; (39)The precedence of the above classifications is programmable; (40)Supports IEEE 802.3ad link aggregation; (41)8 groups of up to 8 ports per group; (42)Allows trunking of ports located on cascaded chip; (43)Supports load sharing among trunked ports based on: Source port, Source and/or destination MAC address; (44)Supports module hot swap on all ports; (45)MIB Statistics counters for all ports; (46)Full Duplex Ethernet IEEE 802.3x Flow Control; (47)Backpressure flow control for Half Duplex ports; (48)Hardware auto-negotiation through MII management interface (MDIO) for Ethernet ports; (49)Built-in reset logic triggered by system malfunction; (50)Built-In Self Test for internal SRAM; (51)IEEE-1149.1 (JTAG) test port.
Diagrams
 |
 ZL50010 |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 |
 ZL50011 |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 |
 ZL50012 |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 |
 ZL50012/GDC |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 |
 ZL50012/QCC |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 |
 ZL50012QCG1 |
 Other |
 |
 Data Sheet |
 Negotiable |
|
||||
 (China (Mainland))
(China (Mainland))







